IoT Sensor Selection: Best Practices for Building Automation
A comprehensive guide to choosing the right sensors for occupancy detection, air quality monitoring, and energy metering in modern smart buildings.
Introduction
Sensors are the eyes and ears of smart buildings. Choosing the right sensors for your building automation project is critical to achieving accurate data, reliable operation, and return on investment.
Sensor Categories for Smart Buildings
Occupancy and Presence Detection
Passive Infrared (PIR)
- Best for: Simple presence detection in enclosed spaces
- Pros: Low cost, easy installation, privacy-friendly
- Cons: Cannot count occupants, blind spots possible
Ultrasonic Sensors
- Best for: Areas with obstructions or partitions
- Pros: Works around corners, reliable detection
- Cons: Can be triggered by air movement
Radar/Microwave Sensors
- Best for: Large open areas, through-wall detection
- Pros: Covers large areas, works through materials
- Cons: Higher cost, potential false triggers
Computer Vision (Camera-based)
- Best for: Accurate people counting, behavior analysis
- Pros: High accuracy, multiple functions
- Cons: Privacy concerns, processing requirements
CO2 Sensing (Indirect Occupancy)
- Best for: Estimating occupancy levels in shared spaces
- Pros: Also provides air quality data
- Cons: Slow response to changes
Environmental Monitoring
Temperature and Humidity
- Critical for comfort and HVAC control
- Consider accuracy, response time, and placement
Air Quality (CO2, VOCs, PM2.5)
- Important for health and productivity
- Multiple parameters provide comprehensive picture
Light Level
- Enable daylight harvesting strategies
- Consider spectral response and mounting location
Energy Metering
Power Meters
- Sub-metering enables consumption analysis
- Consider accuracy class and communication protocol
BTU Meters
- Track thermal energy for HVAC systems
- Important for tenant billing and optimization
Selection Criteria
Accuracy and Precision
Match sensor accuracy to your application needs. Over-specifying wastes money; under-specifying compromises results.
Communication Protocol
Consider compatibility with your building systems:
- BACnet for traditional BMS integration
- Modbus for industrial applications
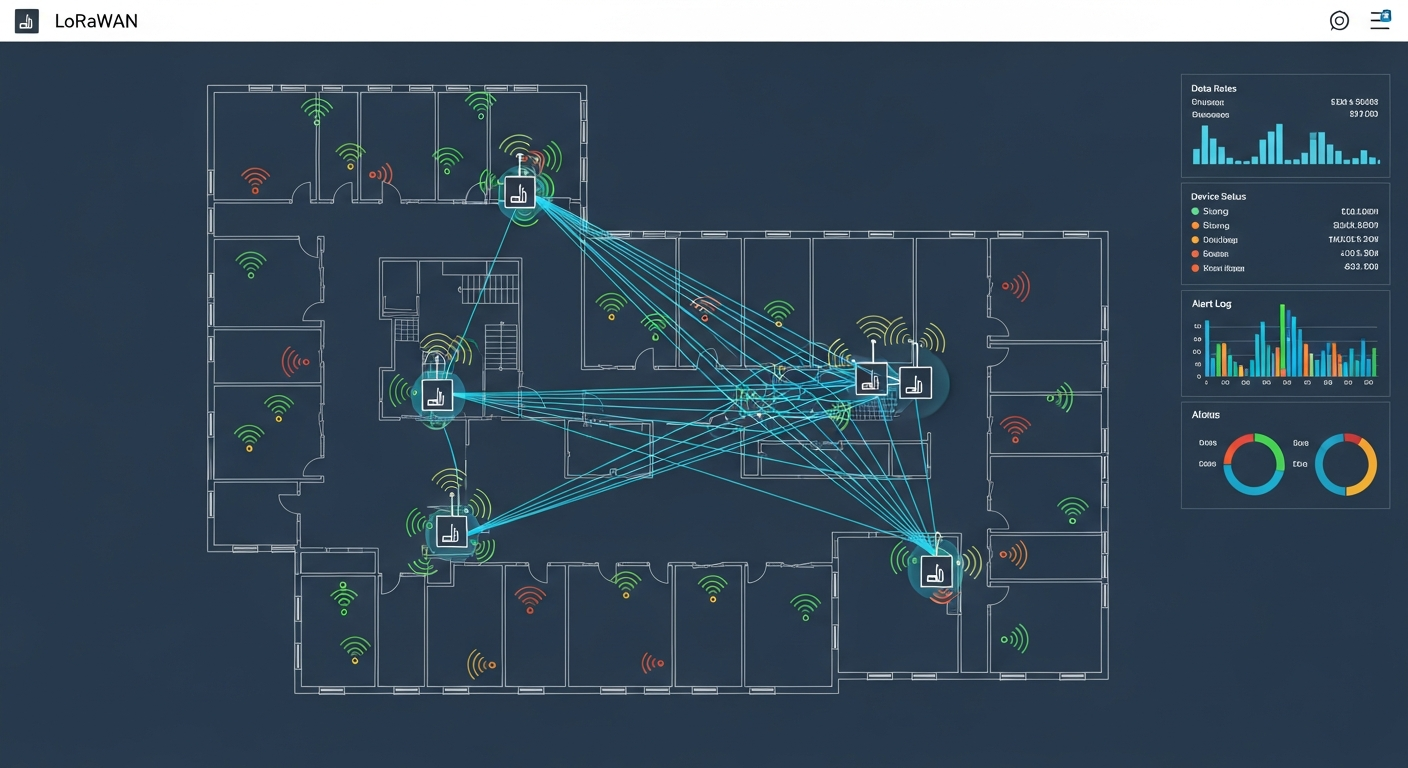
- LoRaWAN for wireless, battery-powered sensors
- MQTT for cloud-connected IoT devices
Power Requirements
Battery-powered sensors offer flexibility but require maintenance. Wired sensors are more reliable for critical applications.
Environmental Rating
Consider operating temperature, humidity, and IP rating for sensor placement location.
Scalability
Choose sensors that can grow with your building portfolio and integrate with modern platforms.
Installation Best Practices
- Follow manufacturer guidelines - Placement affects accuracy
- Document sensor locations - Create a comprehensive sensor map
- Calibrate on installation - Verify accuracy before relying on data
- Plan for maintenance - Battery replacement, cleaning, recalibration
The CONTEXUS Ecosystem
CONTEXUS supports a wide range of sensor protocols and provides unified data management across your sensor infrastructure. Our open architecture means you're never locked into a single vendor's sensor ecosystem.
Conclusion
Thoughtful sensor selection is fundamental to smart building success. Take time to understand your requirements, evaluate options carefully, and choose sensors that will serve your building well into the future.